Fix Django Static Files Permission Problems
One of the most common problems you may encounter when deploying your first Django app is that static files work perfectly in the dev environment with runserver and DEBUG = True, but the moment you try to deploy the site on the production server with a WSGI server and nginx, you get 403 permission errors for static files.
Looking at permissions on your static directory may not show anything obviously wrong, but in my experience, the computer doesn't lie, and your permissions certainly may prohibit nginx from accessing your static files.
About your user
In this article, I will be using a user named ubuntu, as it is commonly used on Ubuntu servers. Please replace it with the name of the user the WSGI (or ASGI) server runs as.
Common cause of the permission denial
Depending on the guides you followed while building and deploying your app, you may have your STATIC_ROOT defined as follows:
1 2 3 | |
and you may have deployed your app as your own user, e.g. ubuntu, under your own home directory (/home/ubuntu/myapp). Finally, you installed and configured nginx with the a location block similar to:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
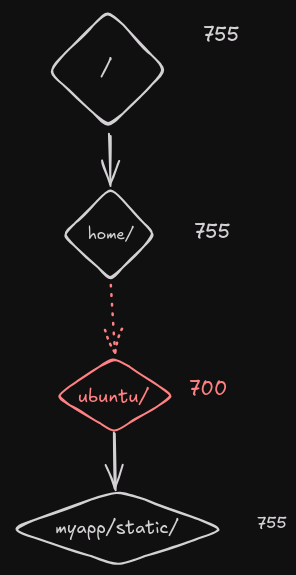
While Django, running as the ubuntu user, will happily write static files to that directory, and that particular directory may be world-readable, most Linux distros assign permissions like 700 or 750 to users' home directories, meaning that other users cannot access them, which is important to safeguard your data. You can verify the permissions as follows:
1 2 | |
As you can see, the permissions are set to drwxr-x---. As nginx normally runs under its own system user (httpd, nginx, www-data, or similar), it will get its permissions from the other group, in this case, --- meaning it cannot read, write, or execute the directory. In order to access any directory, the user also needs the appropriate access to all parent directories, so the permissions on the myapp and static subdirectories are irrelevant.
How to fix it
The easiest and most secure solution is to simply move the static files directory to a location outside your user's home so nginx may access it. Two common options are under /srv/http/ or /var/www/. Let's create a directory owned by ubuntu so collectstatic may write to it.
1 2 | |
Next, we need to update the Django settings to reflect those changes.
1 2 | |
Then we need to update the nginx settings.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
We restart the WSGI server and nginx. Assuming you run nginx via systemd:
1 | |
Finally, run collectstatic and hopefully the issue will be resolved.
Aug. 30, 2024, 3:18 p.m.
Tags